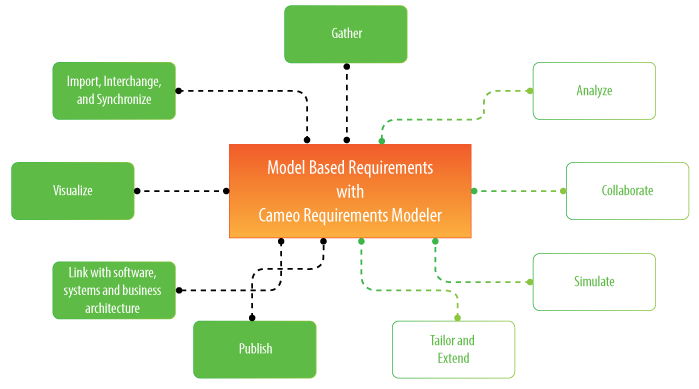
Model-based requirements engineering brings the value of:
- Easy identification of the scope and potential consequence of any change.
- Single and consistent data source: requirements, processes, and design.
- Increased quality of requirements due to the automatic validation and better visibility.
- Saved time and resources as you are working in the same environment where your models are.
- Improved team communication with a simple and standard notation, clear diagrams, and a web-based report.
With this plugin you can:
- Import requirements in a ReqIF file from other requirements management tools, such as IBM DOORS 9.4 and 9.5, IBM DOORS Next Generation, PTC Integrity, Polarion, and Siemens Teamcenter.
- Trace from requirements to other model elements of business, software, or systems architecture and align requirements with your model.
- Analyze the impact of a change.
- Track metrics.
- Capture requirements in dedicated diagrams, matrixes, and tables.
- Document requirements.
- Extend the plugin by creating new requirement types and customizing the plugin’s functionality.
For more information, visit the Cameo Requirements Modeler Plugin page.
Glossary saves time by ensuring consistent usage of terminology in the organization. It also improves the communication between team members since terms are understood in the same way and definitions become visible everywhere the terms are used.
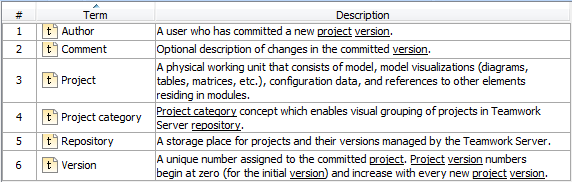
Creating a term is quick and easy. Just do one of the following:
- Add any word or phrase to the glossary while typing or editing.
- Drag any element you wish to become a term to the glossary table.
- Click the Add New or Add Existing button on the glossary table toolbar.
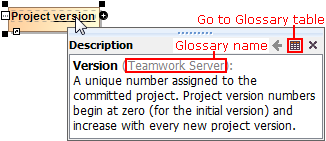
After terms are defined in the glossary, it is easy to use them in your project. Just press Ctrl+spacebar while typing to get a list of available terms.
For your convenience, a term description becomes visible when you move the pointer over this term.
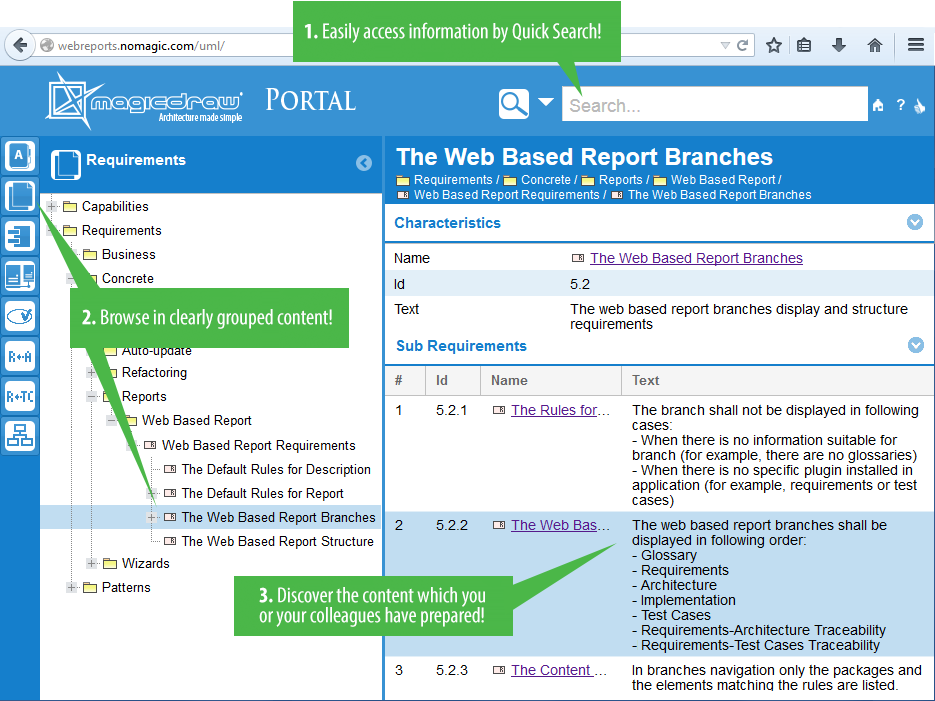
Publish your project as interactive web portal and share it with stakeholders, including even those who are incapable of reading models in MagicDraw!
The published web portal eliminates less needed elements from the model tree and proposes the most relevant views of software engineering project, such as Glossary, Requirements, Architecture, and Implementation. So you can discover your project in user-friendly and easily browsable environment.
Use quick search to find elements and diagrams for viewing their custom contents and share this information with colleagues. Provide feedback on any element or diagram.
Publishing the project as a web portal is as easy as generating any report. On the main menu, click Tools > Report Wizard, select the Software Engineering Portal template, and follow the steps of the report wizard. Then place the output in a shared directory or on web server to make it available for colleagues.
IMPORTANT! The Software Engineering Portal template is only available in MagicDraw Enterprise edition. In other editions, MagicDraw provides a demo version of this web report template, which can contain, at most, 10 symbols per view.
NOTE. This is a technology preview of the software engineering portal. Please explore this new portal, experiment with it, and get back to us at support@nomagic.com with your feedback and suggestions about possible improvements or features you are missing. We seek to create as serviceable tool as it could be, so we are thankful and very appreciative of your contributions!
With this new approach you can
- Create metric suites for calculating metrics.
- Calculate metrics according to given parameters.
- Easily customize the representation of the metrics in the new type table – the metric table.
Creating a new elementary metric suite is as simple as creating a new class with a couple of stereotyped attributes: one for parameter definition and one for metric definition.
The parameter definition can be any model element or a primitive type, such as real or integer. The metric definition, that is, a formula for calculating metrics, can be easily specified either as a structured expression (by using the operations of the expression evaluation engine) or as a script operation written in any script language supported by MagicDraw (for example, JavaScript, Jython, Groovy). Moreover, one metric definition can use the results of other metric definitions.
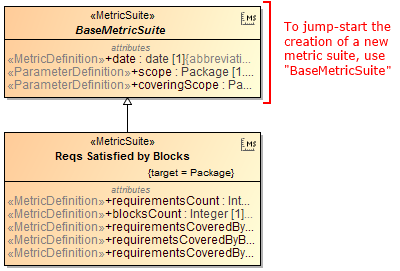
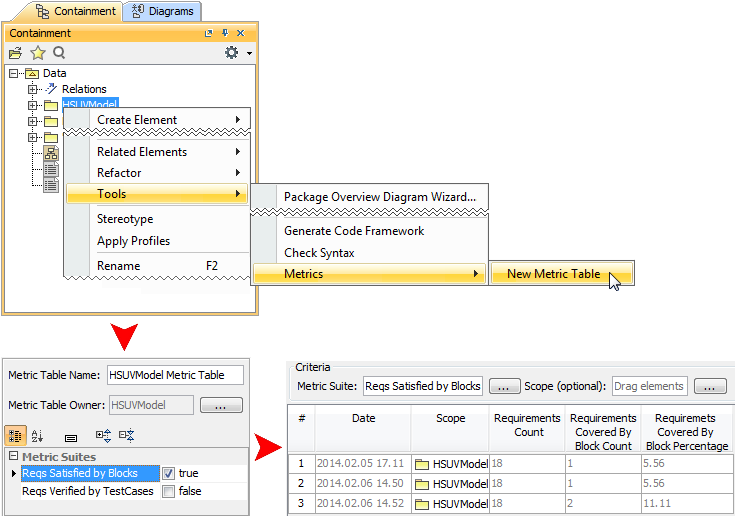
Once the metric suite is created, you can calculate the metrics for a selected element. Analyze the results of the calculations, that is, metrics, in a metric table, which is automatically created for these metrics representation. You can easily reorganize the columns of the table, calculate new metrics, and recalculate the existing metrics with other parameters.
The recent enhancements for modeling efficiency saves time, which allows focusing on what to model, but not how to model and keep the result well-formed:
- Drawing paths does not require manual support for the path layout optimization. The path automatically chooses the optimal route. Learn more
- Browsing diagrams in the same tab reduces the number of open unneeded diagrams and enables effective navigation through different aspects of the model side-by-side. Learn more
- Creating a new diagram is no longer a challenge with the new Create Diagram dialog designed to minimize the time spent looking for the proper menu command or toolbar button, especially if you have plugins installed. Learn more
- Simplified and unified UI for symbol manipulation makes the symbol customization easier and intuitive. Learn more
- Slight changes in compartments behavior make your work with diagrams easier and simpler. Learn more
- Scope selection enables automatic update of tables. Learn more
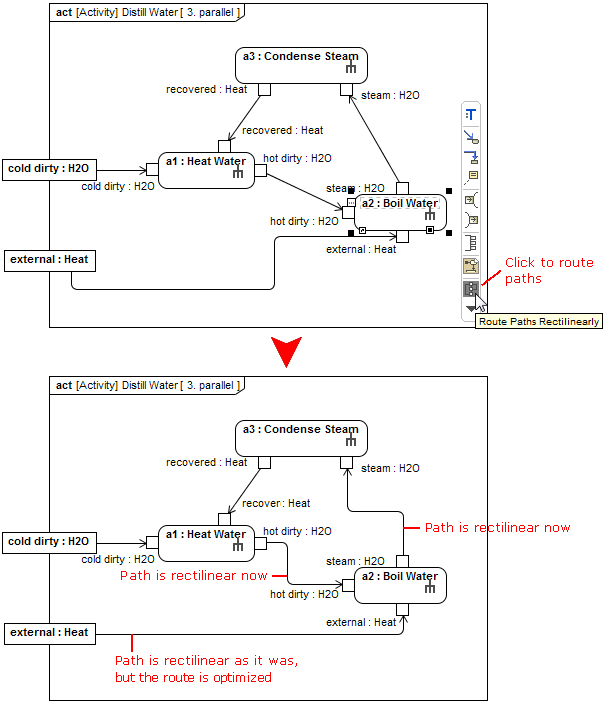
Smarter path layout
Now you can get professional-looking diagrams quickly, without the need to adjust the path layout manually. When drawing new paths, reconnecting or moving paths, or resizing connected shapes, the automatic layout does most of the work in optimizing the routes for these paths, so you can focus on model creation.
Here are the rules of the new path behavior:
- The path always chooses the optimal route.
- When reconnecting the path end to a nearby shape, the existing breakpoints of the path persist. However, if the path route changes a lot, the path is re-laid out.
- When drawing a new path or reconnecting path ends, the path overcomes obstacles.
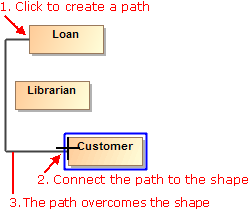

- If there are obstacles on the shape border (for example, Ports, Pins, paths), the path end is centered according these obstacles.
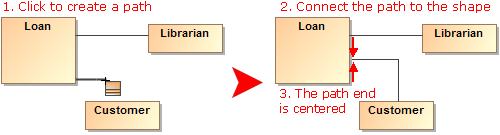
- If there are obstacles on the shape border (for example, Ports, Pins, paths), new paths overcome these obstacles.
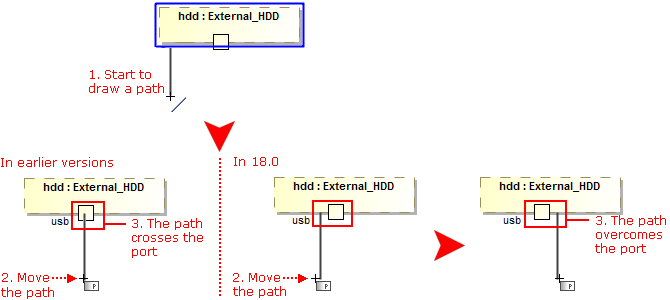
- Path ends avoid connecting to the shape corners. Moreover, the path ends are centered considering the obstacles on the shape border or nearby shapes.
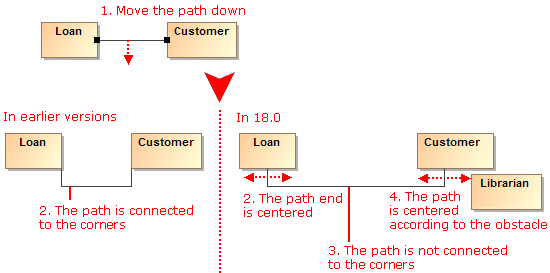
- The path end can be connected to the right or bottom border of the shape.
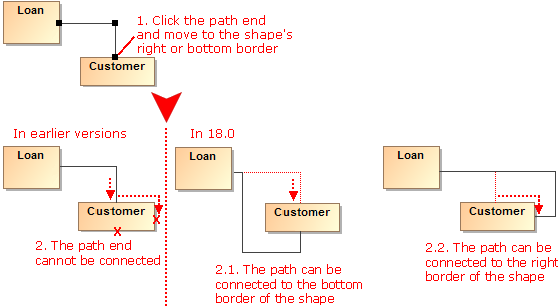
- After switching positions of shapes, path ends become glued to the closest borders.
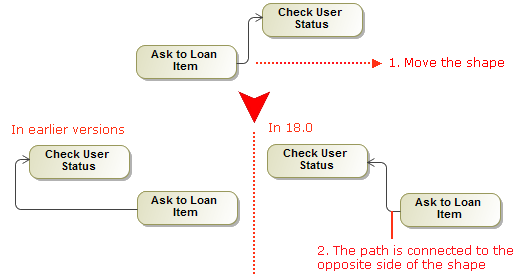
- The path end can be moved up and down or to the left or right on the shape border.
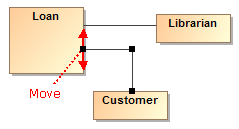
Also, now you can make the route of a single path or the routes of all the paths connected to a selected shape rectilinear with just one click.
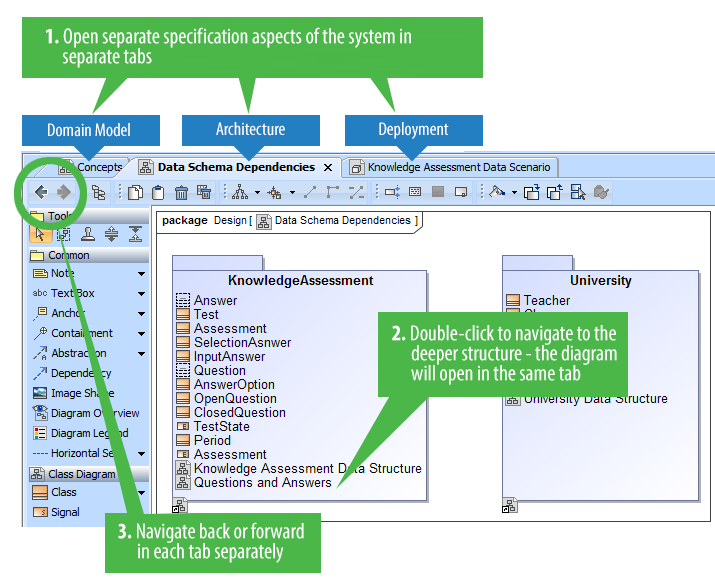
Tabbed browsing between diagrams
Got lost between open diagrams? In earlier versions, every diagram could open only in a new tab. Now you can choose to open diagrams either in the same tab or in a new tab – just like in the most popular Internet browsers.
Here are the benefits of using the tabbed browsing:
Different aspects of the system (for example, requirements, architecture, test cases, domain models) can now be analyzed in separate tabs. Both backward and forward navigations are supported for each aspect (tab) separately. Navigation does not open new tabs by default, which greatly helps in limiting the number of open tabs.
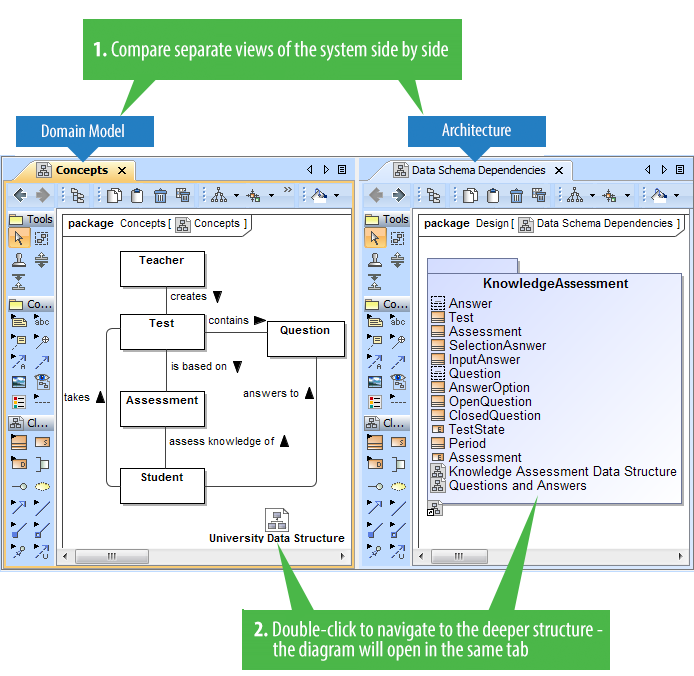
- Ability to compare separate views of the system side-by-side. For example, business and IT architectures can now be displayed in two tabs side-by-side and analyzed by drilling down in their hierarchies. Navigation deeper in the structures will not open new tabs, which allows the smooth analysis of the modeled system.
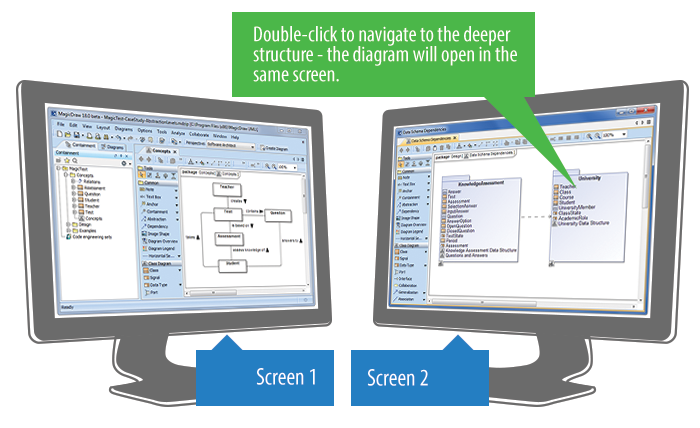
- Smooth work with multiple screens. Browsing in a tab of the second screen never opens diagrams in the first screen, which means you stay in the same screen. New tabs open in the same screen, to the right of the active one.
New Create Diagram dialog
Spending too much time searching for the specific diagram to create? Now you can create any diagram you want in just a few seconds despite the number of diagrams! Simply click the Create Diagram button (or press Ctrl+N), type the first letters or a part of the diagram type name, and press Enter.
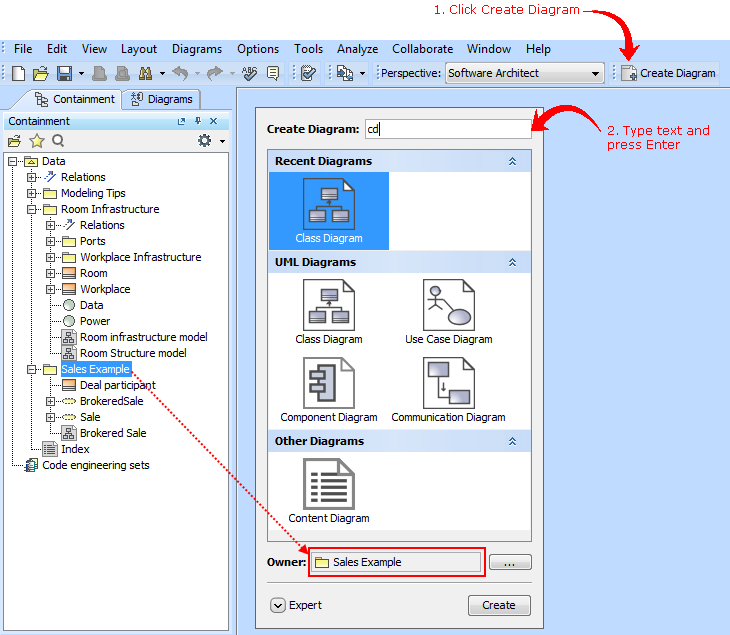
The enhanced Camel Case mode in Search engine makes the diagram creation even faster, as it allows:
- Search using non-capital letters – "ucd" instead of "UCD".
- Skip the spacers – "cv3" works as well as "CV-3" or "cv-3".
- Perform partial search – "ibd" finds SysML Internal Block diagram.
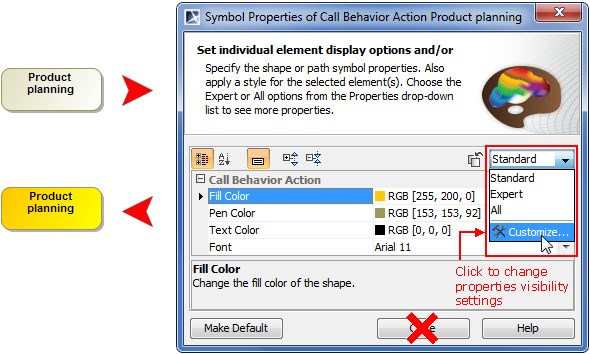
Unified manipulation of symbols
Simplified and unified UI for symbols manipulation makes the symbols customization easier and intuitive:
Now you can see how your shapes or paths changes immediately after modifying their symbol properties without closing the Symbol Properties dialog. Also, while the dialog is open you can still work with diagrams or other dialogs. The ability to group the properties by display modes (Standard, Expert, All) allows the hiding of unnecessary properties, thus making the dialog simpler and faster to use.
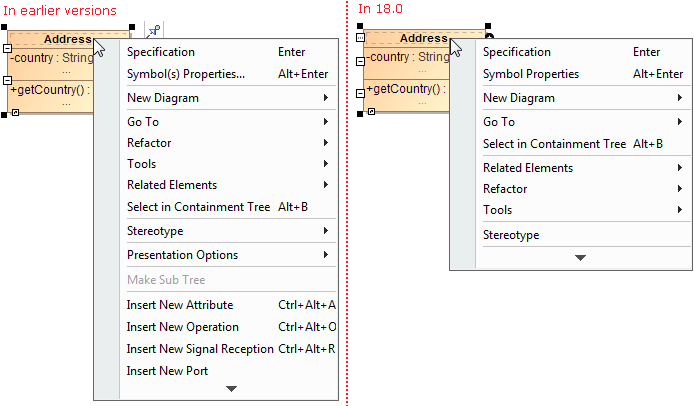
- Lists of properties in the Symbol Properties dialog and on the symbol's shortcut menu are re-arranged and much shorter now. Furthermore, you can customize these lists according to your needs.
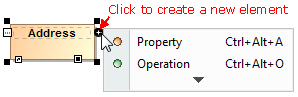
- New smart manipulators enable the faster creation of new elements in compartments as well as easier management of these compartments.
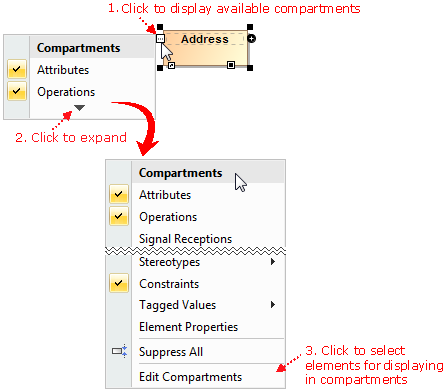
Compartments display changes
- Empty compartments are not displayed on shapes by default.
- Compartment boxes can now display compartment names (for example, attributes, operations). In new projects, compartment names are shown by default. In older projects, you should customize symbol properties.
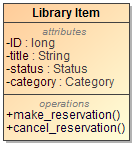
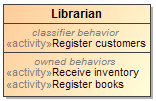
- Behaviors of an element, such as Class, Use Case, or Component, can now be displayed in the compartment on the element's shape. The compartment has two groups: classifier behavior and owned behaviors.
- Ports can now have compartments.
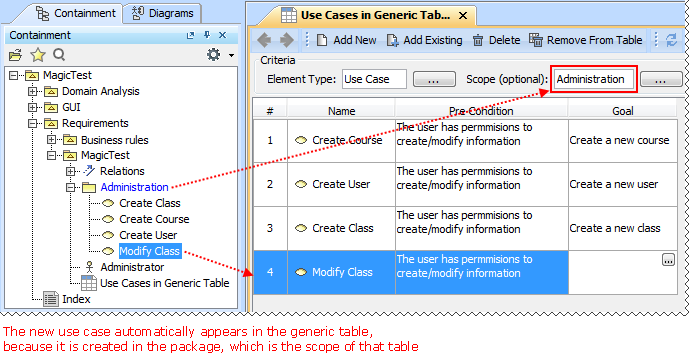
Scope selection in tables
Now you can define any package as scope for your table. All the elements in this package will be automatically added to the table; subsequent elements created in this package will also be added to the table.
Other
Nodes are movable and branches are expandable even in read-only Relation Maps.
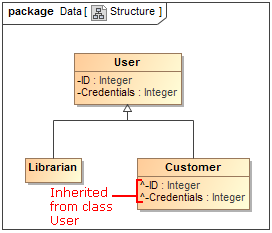
Inherited members, such as attributes, operations, signal receptions, ports, literals, and extension points, can be easily identified on element's shape. They are now denoted with the caret "^" sign.
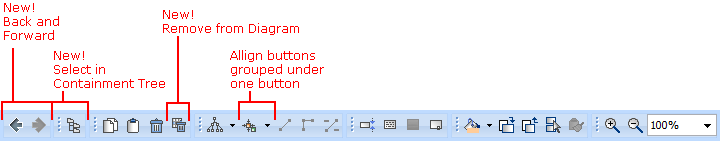
The main toolbar and the diagram toolbar have been reorganized and minimized:
On the main toolbar, the single Create Diagram button has replaced the cumbersome diagram toolbars thus minimizing distractions.

On the diagram toolbar, rarely used buttons have been removed and the groups of buttons have been moved under a single button.
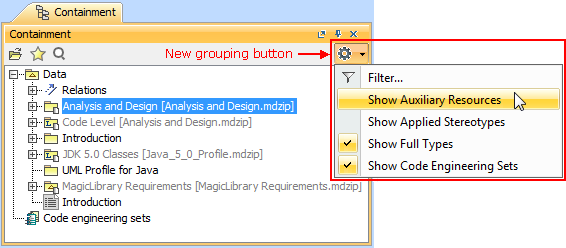
Less used option buttons became commands of the new grouping toolbar button and are now by default hidden.
Drawing several symbols of same type consecutively has been simplified. Now instead of clicking the Sticky button, you can press the Shift key. While holding the Shift key, click the element button on the diagram pallet and then click the diagram pane – with each click, the new symbol of the same type will be created.
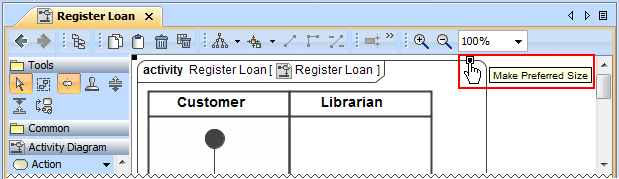
Cannot see the Make Preferred Size smart manipulator on big shapes? Now the smart manipulator is always displayed on any of the visible borders. Just select the shape, and the manipulator appears at the right of the shape’s horizontal border or at the bottom of the vertical shape’s border.
Element shape can now display the image of the element type, such as Activity Parameter Node, Call Behavior Action, Collaboration Use, Instance Specification, Lifeline, Part, Swimlane, or Object Node.
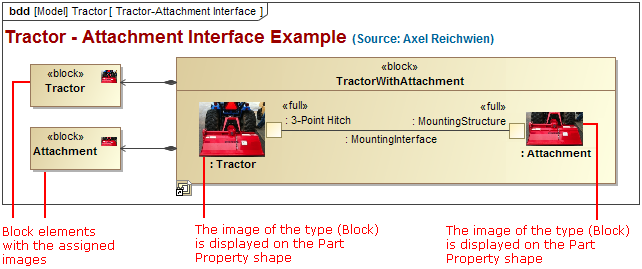
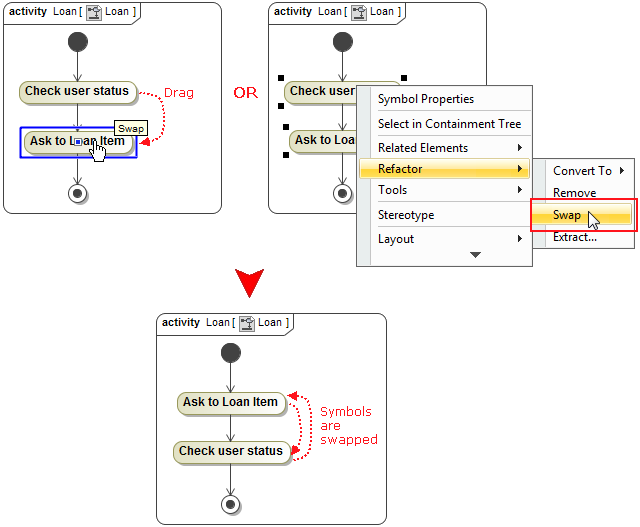
The illustration displays concepts from SysML Plugin.Two connected shapes of the same type can now be easily swapped in Activity or State diagrams.
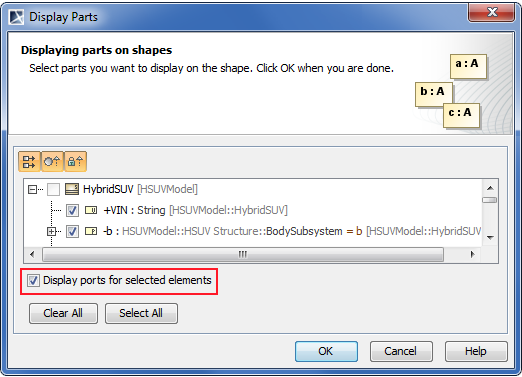
A new option has been added to enable the automatic ports display.
The illustration displays concepts from SysML Plugin.Forget the long workflow when assigning an already created behavior to operation! Now you can now easily create and assign an operation to any owned behavior directly from the Specification window.
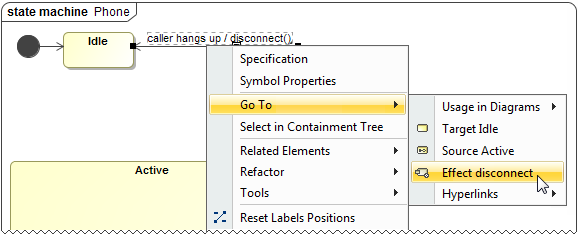
Tracing between the related elements is now easier, since you can navigate:
- From the Transition's shortcut menu to the Effect element.
- From the Connector's shortcut menu to the Conveyed elements.
Dragging an Interaction to an Interaction Use on diagram pane makes the specification of the referred Interaction for this Interaction Use easier.
With the help of an instance table you can easily:
- Review instances of one or more classifiers, in the single place.
- Create instances for one or more classifiers.
- Edit slot values of the instances displayed in the table.
- Customize the representation of the table.
- Export the data into an HTML, XLSX, or CSV file.
All that needs to be done is creating an instance table, adding the instances, and then choosing the slots to review and edit. This form of reviewing and editing data will definitely save a lot of time, as opening the Specification window of each instance is no longer required.
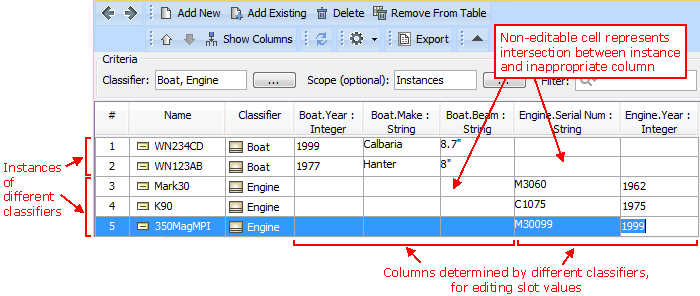
The illustration displays concepts from SysML Plugin.
Other News
Document Modeling Plugin (Technology Preview)
No Magic, Inc. presents a technology preview of Document Modeling Plugin, which the main purpose is to assist in the modeling of the document structure. This plugin is familiar to system engineers as concepts from the OMG SysML standard are used. However, it is designed not only for systems engineers, but also for systems analysts, systems architects, and other persons who need to model a document structure for the specific project.
Document Modeling Plugin allows reviewing the prepared document structure in the document preview dialog and saving the document as a .pdf, .html, or .xml file. This plugin also allows you to:
- Use a standardized way to create a document structure model.
- Create a document structure in a dedicated diagram.
- Preview your document in a preview panel.
- Share a document structure model with your colleagues via Teamwork Server.
- Apply different document styles.
Document Modeling Plugin provides:
- An easy way for defining a document structure and scope.
- A single document structure source: the model of document structure can be shared via Teamwork Server for the use of the entire team.
- Saved time and resources as you are creating a document structure in the same manner as your other projects are created.
NOTE. This is a technology preview of the document modeling functionality. It is not intended for use in the production environment. Please explore this new technology, experiment with it, and get back to us at support@nomagic.com with your feedback and suggestions about possible improvements or features you are missing. We seek to create as serviceable tool as it could be, so we are thankful and very appreciative of your contributions!
Command Line Utility for Teamwork Server Administration
Administrative tasks, such as users, projects, and permissions management, can now be performed by using a new command line utility - teamwork_console.exe.
The ability to access the server administration functions in this new way facilitates the scriptable management of Teamwork Server. This enables the automation of routine administrative tasks, such as permission management, and improves integration with external identity sources. For example, it is now possible to retrieve group information from LDAP servers and set permissions accordingly in MagicDraw Teamwork Server.
Discontinued Compatibilities and Dropped Integrations – Important for OS X users
MagicDraw 18.0 is not compatible with OS X Leopard and Snow Leopard, nor with Java SE 6. Although, Java SE 6 based code engineering is still supported.
MagicDraw 18.0 and Eclipse integration is not supported for OS X. The integration fails to run because of technical issues related to Java SE 7, which is the only Java version compatible with MagicDraw 18.0. Although, the standalone MagicDraw 18.0 runs on OS X with no problems.
MagicDraw 18.0 integration with NetBeans IDE is not supported. If you need this integration, you are welcome to use MagicDraw 17.0.5 or earlier.
Miscellaneous
The obsolete use case numbering is no longer supported, and all the use cases are now numbered using the approach, which is based on the generic numbering mechanism.
Executable files of MagicDraw and Teamwork Administrator's Console are no longer stored in the same location. All the files of Teamwork Administrator's Console have been moved to the collaboration folder in the MagicDraw installation directory. Developers of MagicDraw extensions will no longer be confused trying to determine the right path to the MagicDraw executable file!
File Format Changes
File format has been adopted to UML 2.5 support related changes:
Stored elements format has been changed to reflect minor changes in the metamodel. See Metamodel Changes for details.
URIs have been changed for profiles. The new URIs are as follows:
- xmlns:uml='http://www.omg.org/spec/UML/20131001'
- xmlns:xmi='http://www.omg.org/spec/XMI/20131001'
- xmlns:StandardProfile='http://www.omg.org/spec/UML/20131001/StandardProfile'
- xmlns:MagicDraw_Profile='http://www.omg.org/spec/UML/20131001/MagicDrawProfile'
StandardProfileL2 and StandardProfileL3 have been merged into StandardProfile. All references to any element from these profiles now uses the xmlns:StandardProfile URI.
Open API Changes
UML 2.5 support related changes
- UML metamodel interfaces have been adjusted to UML 2.5 support related changes. See Metamodel Changes for details.
- com.nomagic.uml2.StandardProfileL2 and com.nomagic.uml2.StandardProfileL3 classes have been merged into com.nomagic.uml2.StandardProfile.
UI refactoring related changes
UI of diagrams' windows management, symbols' compartments management, and elements creation in compartments have been refactored. As a consequence, some actions have been removed from the com.nomagic.magicdraw.actions.ActionsID interface and new actions have been added.
IDs of the removed actions are as follows:
- ActionsGroups.NEXT_DIAGRAM_RELATED
- ActionsGroups.PREVIOUS_DIAGRAM_RELATED
- ActionsID.DIAGRAM_NAVIGATION_GROUP
- ActionsID.INSERT_NEW_ATTRIBUTE
- ActionsID.INSERT_NEW_EXTENSION
- ActionsID.INSERT_NEW_LITERAL
- ActionsID.INSERT_NEW_OPERAND
- ActionsID.INSERT_NEW_OPERATION
- ActionsID.INSERT_NEW_PORT
- ActionsID.LINK_EDITING
- ActionsID.METRICS
- ActionsID.OPEN_IN_NEW_TAB_ACTION
- ActionsID.OPEN_LAST_ActionsID.RECENT_DIAGRAMS
- ActionsID.REDO_LIST
- ActionsID.UNDO_LIST
Project Merge related changes
Types of parameters have been changed from Set to Collection, because of performance related improvements in methods of the following interfaces:
- com.nomagic.magicdraw.merge.Change
- com.nomagic.magicdraw.merge.macro.MacroChange
- com.nomagic.magicdraw.merge.RelatedChange
- com.nomagic.magicdraw.merge.macro.RelatedMacroChange
Structured expressions related changes
The com.nomagic.magicdraw.expressions.ExpressionHelper class has been added. It provides utility methods to use in queries defined with the StructuredExpression language (used by smart packages, derived properties in DSL, and so forth).
UML Interactions related changes
The com.nomagic.uml2.ext.jmi.helpers.InteractionHelper class has been added. It provides utility methods to access Interactions part of UML metamodel.