AVAILABLE FROM 18.0 SP13
Annotations in Cameo Concept Modeler (CCM) offer a way to add contextual documentation to model elements, e.g., concept models, concepts, and properties. CCM primarily supports two types of annotations: Literal and Internationalized Resource Identifier (IRI) annotations. For a more in-depth explanation of annotations, please refer to Annotation and annotation properties.
- An «IRI Annotation» is a use of an IRI, whereas a «Literal Annotation» of any URI type is a mention of an IRI.
Two types of annotations primarily supported in CCM: Literal and IRI annotations.
- A literal annotation provides a data value, e.g., particular string or an integer, that optionally specifies language or datatype of the value.
- An IRI annotation specifies an IRI to annotate a model element.
Annotations are stereotyped as either «Literal Annotation» or «IRI Annotation» to identify the type of the annotation value.
More on Literal Annotation
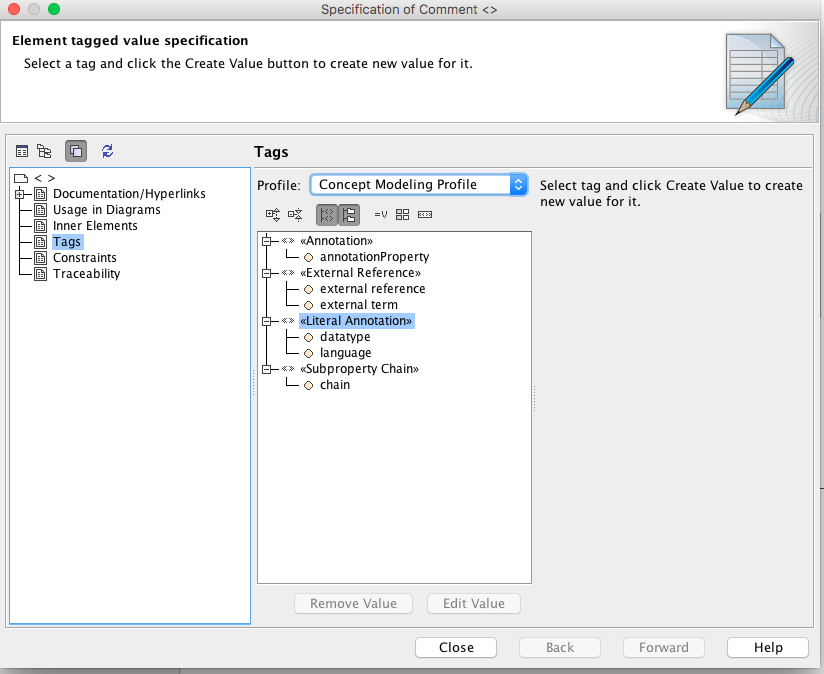
You can specify datatype or language in the Literal annotation’s specification.
Datatype and language can be specified in the literal annotation’s specification.
Importing and Exporting Annotations
- A concept model can be specified as an annotated element, like a concept or a property, for an annotation.
- When the concept model is exported to OWL, the annotation will be on the ontology which corresponds to the exported concept model.
Exporting Annotations
When a concept model is exported to OWL:
- The stereotyped UML comments will be exported as OWL annotations.
- UML comments that are not stereotyped as annotations will be ignored.
- IRI annotations are not lost on importing and exporting.
- Similarly, when an ontology with annotations annotating the ontology itself is imported to CCM, the resulting concept model will contain the annotations that annotated the original ontology.
Importing Annotations
An annotation on an ontology, when that ontology is imported, is converted to an annotation on the concept model which corresponds to that ontology.