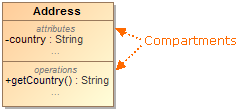
The compartment is area on the shape or next to the shape that is dedicated for the specific type of information.
There are the following types of compartments:
- Compartment boxes. For example, the class shape has compartments which puts attributes, operations, signals into boxes.
- You can hide compartments by suppressing them or expand the hidden compartments to see their data.
- Compartment names are displayed by default. However, you can hide them by changing their visibility settings either in the Symbol Properties dialog or the Project Options dialog. Each compartment has its own property for visibility settings (for example, Show Attributes Compartment Name).
- Compartments that are displayed next to the element name on the shape. For example, a shape has a compartment stereotypes, constraints, and others.
- Stereotypes (or stereotypes compartment) are displayed above the element name.
- Constraints (or constraints compartment) are displayed under the element name.
- By default, tagged values are displayed under the element name or you can select to display tagged values in the compartment box.
- Element Properties are displayed in the compartment box.
- Compartments that are displayed next to the element name, next to the shape. For example, an Actor has a compartment for element properties, a compartment for stereotypes, behaviors, and others.
- Compartments on paths that are displayed next to the path label. For example, a compartment for element properties, a compartment for stereotypes, and others.